BibTeX | RIS | EndNote | Medlars | ProCite | Reference Manager | RefWorks
Send citation to:
URL: http://journal.iehfs.ir/article-1-740-en.html
2- Assistant Professor, Department of Wood and Paper Sciences & Technology, Faculty of Natural Resources, College of Agriculture and Natural Resources, University of Tehran, Karaj, Iran , pmoradpour@ut.ac.ir
3- Department of Occupational Health, School of Health, Mazandaran University of Medical Sciences, Sari, Iran
4- Faculty Member, Department of Wood and Paper Sciences & Technology, Faculty of Natural Resources, College of Agriculture and Natural Resources, University of Tehran, Karaj, Iran
Students spend most of their time at school in classrooms, sitting; therefore, the use of inappropriate educational furniture may cause them discomfort and predispose them to musculoskeletal disorders (MSDs) [3].
Field research shows that the spine problem of about 6.75 million German employees is caused by chairs that they sat on for 10 hours a day as a child [7].
Therefore, the aim of this study was to investigate the lack of agreement between anthropometric characteristics of students and dimensions of educational furniture and design and manufacture of ergonomic educational furniture separately based on anthropometric characteristics measured in a sitting position on the campus of Agriculture and Natural Resources, University of Tehran. In this study, with the aim of reducing the possible incompatibility and problems of MSDs and improving the change of physical condition in students, ergonomic educational furniture was designed and made of wooden chairs with double sloping seating and Erasmus desk in accordance with it, which can be another innovation of this research.
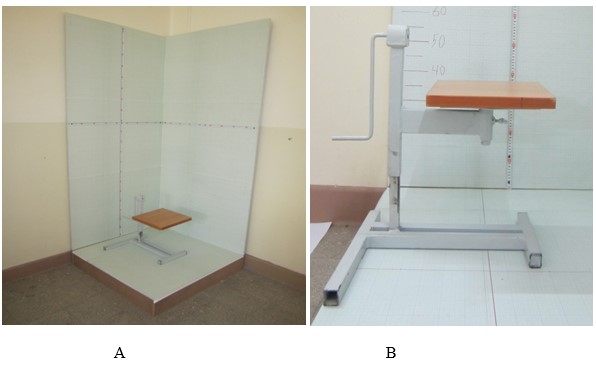
Figure 1: Anthropometric characteristics measuring equipment a) Anthropometric stadiometer, b) Anthropometric chair
In this research, 18 anthropometric characteristics including the popliteal height, knee height, shoulder height, eye height, sitting height, elbow support height, elbow height, knotted elbow length, hip-popliteal length, hip-knee length, thigh thickness, abdominal depth, chest depth, hip width, shoulder width, the transverse width of the elbows, height, and as well as weight for 260 students (130 girls and 130 boys) aged 18 to 35 years were investigated. To collect data, an anthropometric chamber and chair were used. The collected data were analyzed using SPSS software version 20 (SPSS Inc., Chicago, IL., USA). Finally, according to the measured physical dimensions of the students, the Dimensions of ergonomic desk and chair were calculated and designed according to the INSO 9697-1 standard.
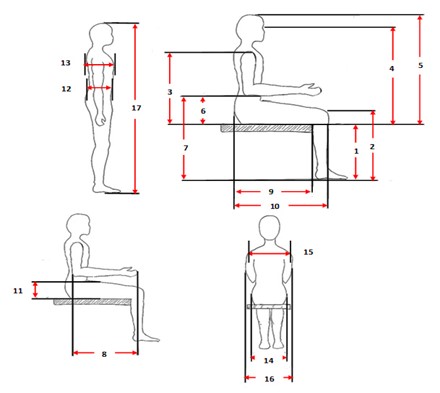
Figure 2. Schematic images of anthropometric characteristics measured in this study: 1- Popliteal (ridge) height, 2- Sitting knee height, 3- Sitting shoulder height, 4- Sitting eye height, 5- Sitting height, 6- Elbow support height Sitting, 7- Height of sitting elbow, 8- Length of elbow-clenched fist, 9- Length of hip-flexion, 10- Length of hip-sitting knee, 11- Thickness of thigh, 12- Depth of abdomen, 13- Depth of chest, 14- Width Sitting buttocks, 15- shoulder width, 16- elbow width, 17- height
Figure 3. Design of separate educational furniture for construction in this research of the type of high chair with a double-sided seat and Erasmus desk
Anthropometric dimensions of students were obtained through mean, minimum, maximum, standard deviation, mean, and the percentile value of 2.5 to 97.5 using SPSS version 20 software. The results showed that the age of the user does not have a significant effect on the size of the desk and the chair. Also, the results showed that there was a significant difference in popliteal height between girls and boys.
| Variable | Gender | N | M | SD | Level of significance |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Popliteal height (cm) | Boy | 130 | 45.31 | 2.27 | 0.001< |
| Girl | 130 | 43.38 | 2.90 | ||
| Knee height (cm) | Boy | 130 | 55.36 | 2.49 | 0.001< |
| Girl | 130 | 49.63 | 6.87 | ||
| Shoulder height (cm) | Boy | 130 | 62.49 | 4.58 | 0.001< |
| Girl | 130 | 58.11 | 3.89 | ||
| Eye height (cm) | Boy | 130 | 79.37 | 5.86 | 0.001< |
| Girl | 130 | 73.16 | 4.42 | ||
| Sitting height (cm) | Boy | 130 | 90.06 | 4.24 | 0.001< |
| Girl | 130 | 84.01 | 4.07 | ||
| Elbow support height (cm) | Boy | 130 | 25.16 | 3.19 | 0.001< |
| Girl | 130 | 23.80 | 2.75 | ||
| Elbow height (cm) | Boy | 130 | 70.38 | 3.67 | 0.001< |
| Girl | 130 | 67 | 4.64 | ||
| Punched elbow length (cm) | Boy | 130 | 38.06 | 2.85 | 0.001< |
| Girl | 130 | 34.49 | 2.53 | ||
| Popliteal-bottock (cm) | Boy | 130 | 48.56 | 3.72 | 0.007< |
| Girl | 130 | 47.53 | 3.06 | ||
| Knee hip length (cm) | Boy | 130 | 59.90 | 3.07 | 0.001< |
| Girl | 130 | 54.78 | 3.09 | ||
| Thigh thickness (cm) | Boy | 130 | 15.04 | 2.29 | 0.001< |
| Girl | 130 | 13.10 | 2.81 | ||
| Abdominal depth (cm) | Boy | 130 | 24.24 | 3.66 | 0.001< |
| Girl | 130 | 21.80 | 3.71 | ||
| Chest depth (cm) | Boy | 130 | 23.94 | 2.68 | 0.171 |
| Girl | 130 | 23.55 | 3.27 | ||
| Hip width (cm) | Boy | 130 | 37.96 | 3.40 | 0.001< |
| Girl | 130 | 36.40 | 3.48 | ||
| Shoulder width (cm) | Boy | 130 | 45.56 | 3.19 | 0.001< |
| Girl | 130 | 38.44 | 2.84 | ||
| Elbow width (cm) | Boy | 130 | 49.39 | 5.38 | 0.001< |
| Girl | 130 | 37.70 | 5.30 | ||
| Height (cm) | Boy | 130 | 1777.01 | 5.94 | 0.001< |
| Girl | 130 | 162.26 | 6.38 | ||
| Weight (Kg) | Boy | 130 | 75.55 | 13.05 | 0.001< |
| Girl | 130 | 58.87 | 9.77 | ||
| Age | Boy | 130 | 22.42 | 3.16 | 0.148 |
| Girl | 130 | 23.09 | 3.56 |
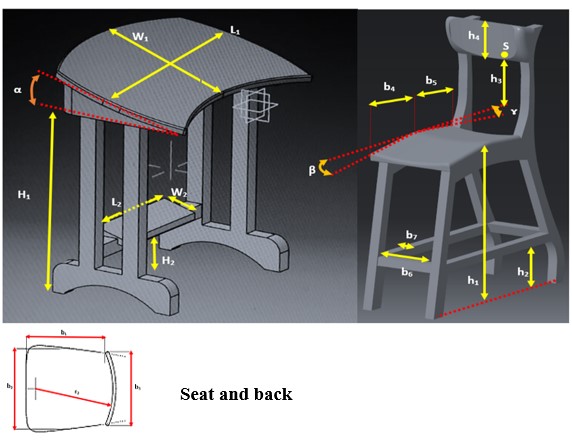
Figure 4. Dimensional guide of a double chair with a slope and a desk suitable for that chair) b1: effective depth of the seat, b2: width of the seat, b3: back width, b4: depth of the front of the seat, b5: depth of the back of the seat, b6: length of the footrest, b7: footrest width, r2: horizontal dorsal radius, h1: seat height, h2: footrest height, h3: point height s, h4: backrest height, b: front seat slope, ɤ: rear seat slope. desk ) H1: desk top surface height, H2: desk top height, L1: desk top surface length, L2: desk top length, W1: desk top surface depth, W2: desk top width, α: desk top surface angle
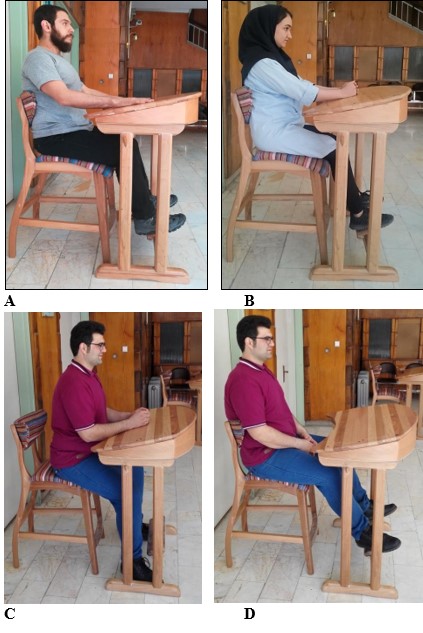
Figure 5. A and B) Ergonomic desks and chairs designed and built after determining anthropometric characteristics for boys and girls
Sitting position: c) while writing (active posture), d) while resting and leaning on a chair (inactive posture)
Table 2. Dimensions of ergonomic desk and chair designed for students of the Campus of Agriculture and Natural Resources, University of Tehran
| Girls | Boys | Variables | Product |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1505-1730 | 1662-1900 | Full range (mm) | Seat |
| 48.67- 38 | 42- 49 | Popliteal range (mm) | |
| +10 | +10 | Minimum slope of the front of the seat (degree) | |
| +15 | +15 | Maximum slope of the front of the seat (degree) | |
| -5 | -5 | Slope of rear seat (degree) | |
| 623 | 660 | Seat height (10%) in (mm) | |
| 420 | 415 | Effective seating depth (mm) | |
| 360 | 377 | Minimum seating width (mm) | |
| 400 | 395 | Seat surface depth (minimum) (mm) | |
| 180 | 197 | S point height (-10 to +20) (mm) | |
| 190 | 190 | Back height (mm) | |
| 330 | 347 | Minimum back width (mm) | |
| 300 | 300 | Minimum horizontal dorsal radius (mm) | |
| 104 | 104 | Back slope (degree) | |
| 243 | 240 | Foot height (mm) | |
| 280 | 240 | Minimum foot length (mm) | |
| 50 | 50 | Minimum foot width (mm) | |
| 940 | 965 | Desk surface height (mm) | Desk |
| 500 | 500 | Minimum depth of desk surface (mm) | |
| 600 | 600 | Minimum desk surface length per person (mm) | |
| 243 | 240 | Foot height (mm) | |
| 300 | 300 | Minimum foot length (mm) | |
| 100 | 100 | Minimum desk foot width (mm) | |
| -20 | -20 | Maximum desk surface angle (degree) |
Considering the difference in dimensions between female and male students, it was found that the popliteal height in the percentile of 5 for boys is 4 cm more than girls. Therefore, using measured anthropometric characteristics, the dimensions of the chair and desk ergonomics were designed in two sizes.
This research was conducted in the form of a master's thesis with the financial support of the scientific deputy of the Faculty of Natural Resources, Campus of Agriculture and Natural Resources, University of Tehran, No. Grant,12-6-30541. The authors of the article consider it necessary to thank and appreciate the cooperation of the Alborz Technical and Vocational Training Center for conducting the best research.
The authors declared no conflict of interest.
Received: 2020/06/8 | Accepted: 2020/08/31 | ePublished: 2020/09/29
| Rights and permissions | |
 |
This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License. |